Content
Antarctic Ozone Layer Shows Signs of Recovery, Says NASA
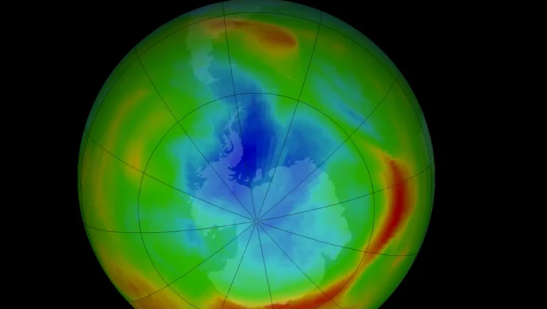
NASA scientists have released a major update revealing significant signs of recovery in the Antarctic ozone layer, one of the most critical shields protecting Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation. This positive shift follows decades of global environmental effort after the discovery of severe ozone depletion in the 1980s.
The new findings indicate that international policies, reduced emissions of ozone-depleting substances, and sustainable climate actions have collectively contributed to stabilizing the ozone layer in the Antarctic region.
What NASA’s Latest Findings Reveal
According to NASA’s atmospheric studies and satellite data, the ozone layer over Antarctica has shown steady improvement over the past decade. This is measured through:
Reduction in the area of the ozone hole
Improved ozone concentration levels
Declining atmospheric levels of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
Stronger seasonal recovery patterns during the Antarctic spring
This progress signals that global environmental agreements, especially the Montreal Protocol, have been successful in reducing substances harmful to the ozone layer.
Why the Ozone Recovery Matters
The ozone layer plays a crucial role in protecting life on Earth:
1. Shields Earth from UV radiation
Improvement helps reduce UV-related risks such as skin cancer, crop damage, and marine ecosystem disruption.
2. Stabilizes climate patterns
Ozone concentration affects atmospheric circulation; its recovery leads to improved climate balance in the Southern Hemisphere.
3. Reinforces success of global climate policies
The ozone layer’s recovery shows that international environmental action works, setting an example for future climate agreements.
4. Promotes long-term environmental sustainability
Healthier ozone conditions contribute to global climate stability and ecological safety.
How Scientists Measure Ozone Recovery
NASA uses a combination of:
Polar-orbiting satellites
Atmospheric monitoring instruments
Ground-based research stations
Stratospheric data analysis
The measurements indicate that if the current recovery pace continues, the ozone layer over Antarctica may return to pre-1980 levels within the next few decades.
Global Impact and Future Outlook
The ozone recovery is one of the most successful environmental turnaround stories in modern history. However, scientists emphasize the need for:
Continued compliance with ozone-protection agreements
Monitoring illegal emissions of CFC-11 and similar chemicals
Supporting climate-friendly technologies
Strengthening global environmental research
If international cooperation remains strong, the ozone layer will continue rebuilding, contributing to safer living conditions worldwide.
FAQs
1. What is causing the Antarctic ozone layer to recover?
Declining use of ozone-depleting substances such as CFCs, thanks to global agreements like the Montreal Protocol.
2. When will the ozone layer fully recover?
NASA estimates that the Antarctic ozone layer may return to pre-1980 conditions by the mid-21st century if current trends continue.
3. Why is the ozone layer important?
It protects Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation, reducing risks to human health, ecosystems, and the climate.
4. How does NASA monitor the ozone layer?
Through satellite imaging, atmospheric monitoring sensors, and global observation systems that track ozone concentration.
5. What would happen if ozone depletion continued?
Higher UV radiation would lead to increased skin cancer rates, ecosystem damage, weakened immune systems, and global climate disruption.
Published on : 25 th November
Published by : Reddy kumar
Credit: Written by Vizzve Finance News Desk
www.vizzve.com || www.vizzveservices.com
Follow us on social media: Facebook || Linkedin || Instagram
🛡 Powered by Vizzve Financial
RBI-Registered Loan Partner | 10 Lakh+ Customers | ₹600 Cr+ Disbursed