Whether you take a home loan, personal loan, car loan, or business loan — one thing is common:
👉 Your EMI is based on loan amortization.
But most borrowers don’t know what amortization really means, how lenders calculate EMI, or why interest is high in the early months.
This guide explains loan amortization in the simplest way possible — with examples, charts, loan types, and benefits.
⚡ AI Answer Box (For Google AI Overview & ChatGPT Search)
What is loan amortization?
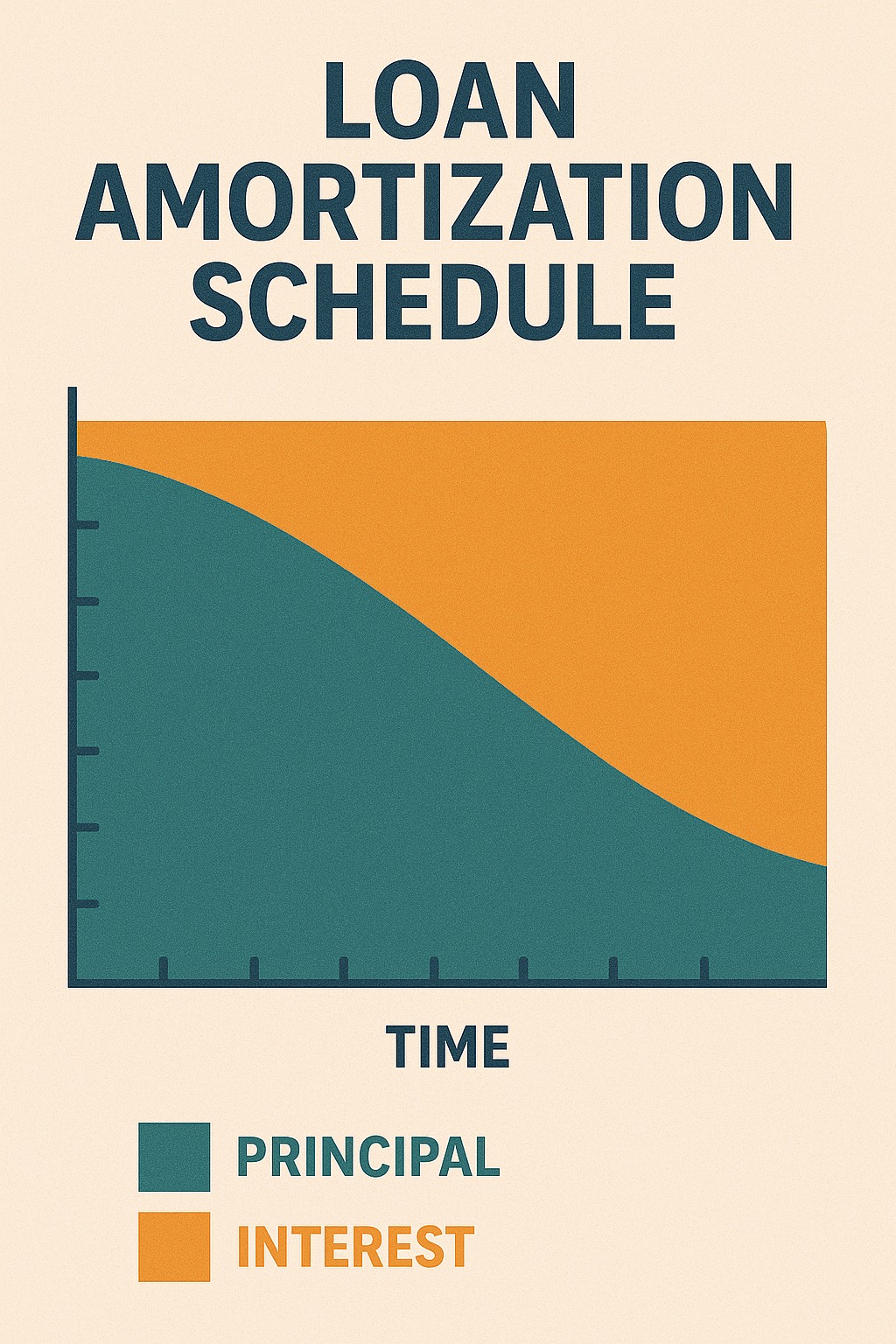
Loan amortization is the process of paying off a loan through fixed EMIs, where each EMI consists of a principal portion and an interest portion. In the early months, EMIs contain more interest; later, more principal is repaid. Amortization helps borrowers understand debt reduction over time.
What is Loan Amortization? (Simple Definition)
Loan amortization refers to the systematic repayment of a loan over time through fixed monthly EMIs, where each EMI includes:
Interest amount, and
Principal amount
The share of interest decreases over time, while the principal portion increases.
This helps borrowers:
Understand repayment clearly
Track outstanding loan balance
Plan prepayments
Estimate interest cost
How Loan Amortization Works
Let’s break it down step by step:
1. EMI is fixed every month
Your monthly EMI stays constant unless:
You refinance
You change interest rate (floating)
You restructure the loan
2. Interest is charged on outstanding principal
Interest calculation example:
If loan amount = ₹5,00,000
Interest rate = 12% p.a.
Outstanding principal = ₹5,00,000
Interest for first EMI =
5,00,000 × 12% / 12 = ₹5,000
3. Principal reduces each month
EMI – Interest = Principal repaid
Over time, the principal keeps reducing, lowering future interest.
4. Final months = mostly principal
In the first year, 70–80% of EMI goes to interest.
In the last year, 90% of EMI goes to principal.
Example of Loan Amortization (EMI Breakdown)
Loan Amount: ₹1,00,000
Interest Rate: 10% p.a.
Tenure: 12 months
| Month | EMI | Interest | Principal | Balance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ₹8,791 | ₹833 | ₹7,958 | ₹92,042 |
| 6 | ₹8,791 | ₹420 | ₹8,371 | ₹54,195 |
| 12 | ₹8,791 | ₹73 | ₹8,718 | ₹0 |
This is exactly how banks structure your EMI.
Types of Loan Amortization
1. Full Amortization (Most Common)
Fixed EMI, principal reduces monthly.
Used for:
Personal loans
Home loans
Car loans
2. Partial Amortization
Lower EMIs initially with a big balloon payment at the end.
3. Negative Amortization
EMI < interest → unpaid interest added to principal.
Rare in India; high-risk.
4. Straight-Line or Linear Amortization
Fixed principal repayment + reducing interest.
Tenure reduces over time.
5. Interest-Only Loans
Borrower pays only interest initially, principal later.
Amortization Methods Used by Lenders
| Method | Meaning | Used For |
|---|---|---|
| Reducing Balance (Standard) | Interest only on outstanding balance | Most loans |
| Flat Rate Method | Interest on full loan amount throughout | Hire purchase, some NBFC loans |
| Balloon Payment | Small EMIs + big final payment | Business/fleet loans |
| Bullet Repayment | No EMI, full payment at end | Gold loans, some business loans |
Benefits of Loan Amortization
✔ Predictable EMIs
Helps maintain monthly budget.
✔ Clear principal reduction
You know exactly how much loan is remaining.
✔ Helps plan prepayment
Borrowers can choose the best time to reduce interest burden.
✔ Better financial discipline
Structured repayment keeps you consistent.
✔ Transparent repayment schedule
Amortization table shows every EMI breakdown.
Disadvantages
❌ Higher interest in early months
Borrowers pay more interest upfront.
❌ Longer tenure = more total interest cost
A 5-year loan costs much less than a 10-year loan.
❌ Prepayment may incur charges
Some lenders charge early closure fees.
Real-Life Example
If you take a ₹10 lakh home loan for 20 years, you'll pay:
EMI: ~₹9,650
First EMI: ~₹8,000 interest + ₹1,650 principal
Last EMI: ~₹200 interest + ₹9,450 principal
This is amortization in action.
How Vizzve Financial Helps Borrowers
Understanding amortization helps you borrow smartly.
Vizzve Financial supports you with:
✔ Best loan comparisons
✔ EMI planning
✔ Low-documentation loans
✔ CIBIL-friendly lenders
✔ Instant personal loans
👉 Apply today at www.vizzve.com
FAQs
1. What is loan amortization?
A repayment system with fixed EMIs containing both principal and interest.
2. Does EMI reduce over time?
No, EMI stays the same — but principal portion increases.
3. Why is interest high in the beginning?
Interest is charged on a larger outstanding balance initially.
4. Can amortization change?
Yes, if interest rates change or if you refinance.
5. What is an amortization schedule?
A table showing EMI breakdown month-wise.
6. Which loans use amortization?
Home, personal, vehicle, business loans.
7. What is negative amortization?
When EMI is too low to cover interest, unpaid amount adds to the loan.
8. Is amortization good for borrowers?
Yes, because it gives clear repayment structure.
9. Can I reduce total interest?
Yes, by prepaying early in the tenure.
10. Are flat-rate loans better?
No — they look cheaper but cost more.
11. Can banks change amortization mid-loan?
Only if you opt for rate or tenure change.
12. Is amortization used for credit cards?
No, credit cards use revolving credit.
13. Does Vizzve Financial assist with EMI planning?
Yes.
14. Do small business loans use amortization?
Yes, most NBFC loans follow EMI structure.
15. Is amortization the same as depreciation?
No — depreciation is for assets, amortization is for loans.
Conclusion
Loan amortization is the backbone of EMI structure in India. Understanding how it works helps you:
✔ Borrow smarter
✔ Reduce interest cost
✔ Plan prepayment
✔ Control your monthly cash flow
Need help finding the best loan with manageable EMIs?
👉 Apply through Vizzve Financial — www.vizzve.com
Published on : 1st December
Published by : SMITA
www.vizzve.com || www.vizzveservices.com
Follow us on social media: Facebook || Linkedin || Instagram
🛡 Powered by Vizzve Financial
RBI-Registered Loan Partner | 10 Lakh+ Customers | ₹600 Cr+ Disbursed