As climate change accelerates, scientists and policymakers are increasingly looking at Carbon Capture, Utilization, and Storage (CCUS) as a critical technology in the fight to limit global warming. While reducing emissions remains essential, carbon capture offers a way to trap CO₂ from major sources—and even directly from the atmosphere—and store or reuse it to prevent it from reaching the atmosphere.
🧪 What Is Carbon Capture?
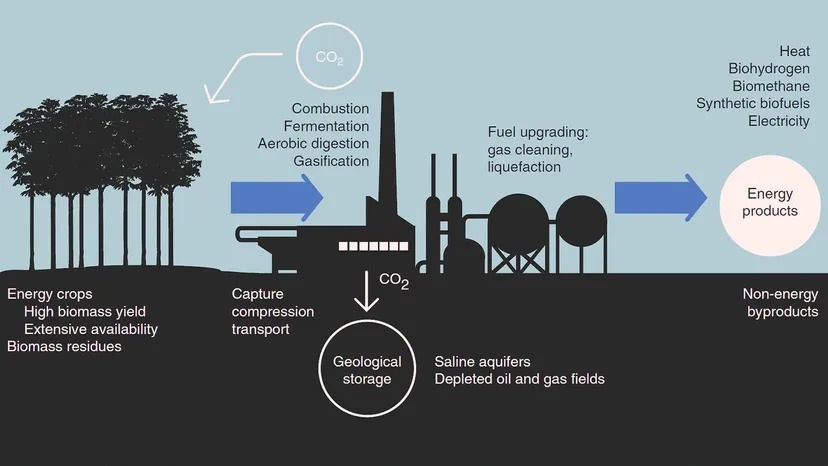
Carbon capture involves trapping carbon dioxide (CO₂) produced by industrial processes like power generation, cement production, and steel manufacturing before it enters the atmosphere. The captured CO₂ is then either:
Stored underground (usually in geological formations like depleted oil fields), or
Used in industrial applications like carbonated beverages, plastics, or synthetic fuels.
🏭 How Does It Work?
Capture
CO₂ is separated from gases produced in electricity generation or industrial processes. Techniques include:
Post-combustion capture
Pre-combustion capture
Oxy-fuel combustion
Transport
The CO₂ is compressed and transported—typically via pipeline—to a suitable storage or utilization site.
Storage or Utilization
Injected into deep rock formations (permanent storage)
Used in enhanced oil recovery (EOR)
Converted into materials like concrete or fuel
🌱 Why Is It Important?
Even with rapid renewable energy adoption, some emissions are unavoidable, especially from industrial sectors. CCUS helps:
Offset emissions from hard-to-abate sectors (steel, cement)
Enable "negative emissions" when paired with bioenergy (BECCS)
Meet global targets like those in the Paris Agreement
🚧 Challenges & Criticism
High cost and energy use
Requires long-term monitoring and regulation
Risk of leakage from storage sites
Critics argue it may delay action on reducing fossil fuel use
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the main goal of carbon capture?
To reduce the amount of CO₂ released into the atmosphere from industrial and power generation sources.
Q2: Is carbon capture a new technology?
No, it's been used since the 1970s in oil recovery but is now being scaled for broader climate mitigation.
Q3: Does carbon capture eliminate the need for renewable energy?
No. It's a complementary solution for sectors where emissions are hard to eliminate.
Q4: Where is carbon captured CO₂ stored?
Typically in deep underground rock formations, such as depleted oil and gas fields or saline aquifers.
Q5: Is carbon capture safe?
With proper monitoring and regulation, carbon storage is considered safe and stable over long periods.
published on 27th june
Publisher : SMITA
www.vizzve.com || www.vizzveservices.com
Follow us on social media: Facebook || Linkedin || Instagram
🛡 Powered by Vizzve Financial
RBI-Registered Loan Partner | 10 Lakh+ Customers | ₹600 Cr+ Disbursed