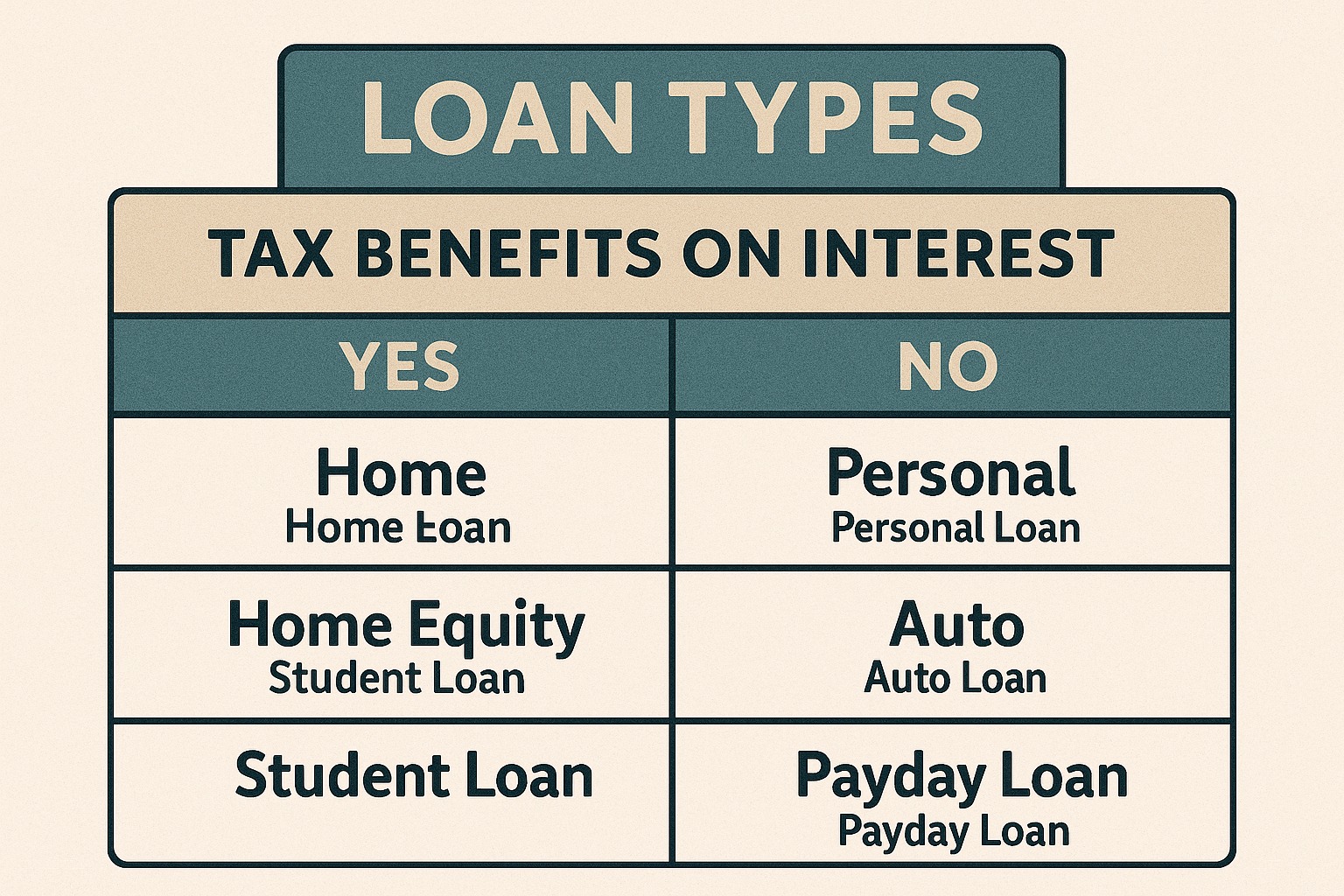
Many people take loans — home loans, personal loans, business loans, car loans, education loans. But not everyone understands the tax implications behind them.
One of the biggest questions borrowers ask is:
👉 “Can I claim tax benefits on the interest I pay?”
The answer: It depends on the type of loan and how you use it.
Here’s a simple and clear guide.
✅ Loans Where Interest IS Tax-Deductible
1. Home Loan (Most Popular Tax Benefit)
A. Section 24(b) — Interest Deduction (Up to ₹2 lakh/year)
For self-occupied property: max deduction ₹2,00,000
For let-out property: no upper limit, but maximum loss set-off = ₹2 lakh
Applicable only on interest component, not principal
B. Section 80C — Principal Repayment (Up to ₹1.5 lakh/year)
Includes home loan principal, stamp duty & registration charges.
C. Section 80EE / 80EEA — Additional Interest (First-time buyers)
Extra deduction available under certain conditions.
2. Education Loan (100% Interest Deduction)
Under Section 80E, entire interest paid on an education loan is tax-deductible for 8 years.
Covers:
Higher education in India or abroad
Courses in any field
Loans taken by self, spouse, or children
No limit on deduction amount.
3. Business Loan / MSME Loan
Interest paid on:
Business loans
Working capital loans
Machinery loans
Cash credit
…is fully tax-deductible as a business expense.
Deduction allowed under:
Section 37(1) → Business expenditure
Section 36(1)(iii) → Interest on borrowed capital
4. Loan Taken for Investing in Property or Shares
If you take a loan to invest:
In rental property → Interest deduction allowed
In shares or mutual funds → Interest allowed as expense under “Income from Other Sources” (with limits)
5. Loan Against Property (LAP) — Condition-Based
If used for business → Interest is tax-deductible
If used for investments → Generally deductible
If used for personal expenses → NO deduction
❌ Loans Where Interest Is NOT Tax-Deductible
1. Personal Loan (Usually No Tax Benefit)
Interest on personal loans is not tax-deductible — except in special cases:
If used for business → deduction allowed
If used for buying/renovating property → interest can be claimed
If used for investments → partially deductible
But for normal use (wedding, travel, shopping, gadgets) → NO tax benefit.
2. Car Loan / Bike Loan
For personal use → No deduction
For business use → Interest is deductible as business expense
3. Credit Card Loans / EMI Conversions
Interest on credit card outstanding is not tax-deductible, unless used for business purchases.
4. Consumer Durable Loans
Loans for:
Electronics
Furniture
Appliances
…do not offer any tax benefits.
Summary Table: When Loan Interest Is Deductible
| Loan Type | Interest Tax-Deductible? | Section |
|---|---|---|
| Home Loan | ✅ Yes | 24(b), 80C, 80EE, 80EEA |
| Education Loan | ✅ Yes | 80E |
| Business Loan | ✅ Yes | 37(1), 36(1)(iii) |
| Loan Against Property | ✔ Sometimes | Depends on usage |
| Personal Loan | ❌ No (except for specific uses) | Depends |
| Car Loan | ❌ No (personal use) / ✔ Yes (business) | Business expense |
| Credit Card Loan | ❌ No (personal) / ✔ Yes (business) | Business expense |
FAQs
1. Is personal loan interest tax-deductible?
Only if used for business, property purchase, or investments. Not for personal spending.
2. Are car loan EMIs tax-deductible?
Yes, for business vehicles. No for personal vehicles.
3. Can I claim tax benefits on two home loans?
Yes — subject to overall Section 24(b) and 80C limits.
4. Is education loan principal tax-deductible?
No. Only interest is deductible.
5. Are credit card EMIs tax-deductible?
No, unless used solely for business.
Published on : 19th November
Published by : SMITA
www.vizzve.com || www.vizzveservices.com
Follow us on social media: Facebook || Linkedin || Instagram
🛡 Powered by Vizzve Financial
RBI-Registered Loan Partner | 10 Lakh+ Customers | ₹600 Cr+ Disbursed