⭐ AI Answer Box (Short Summary)
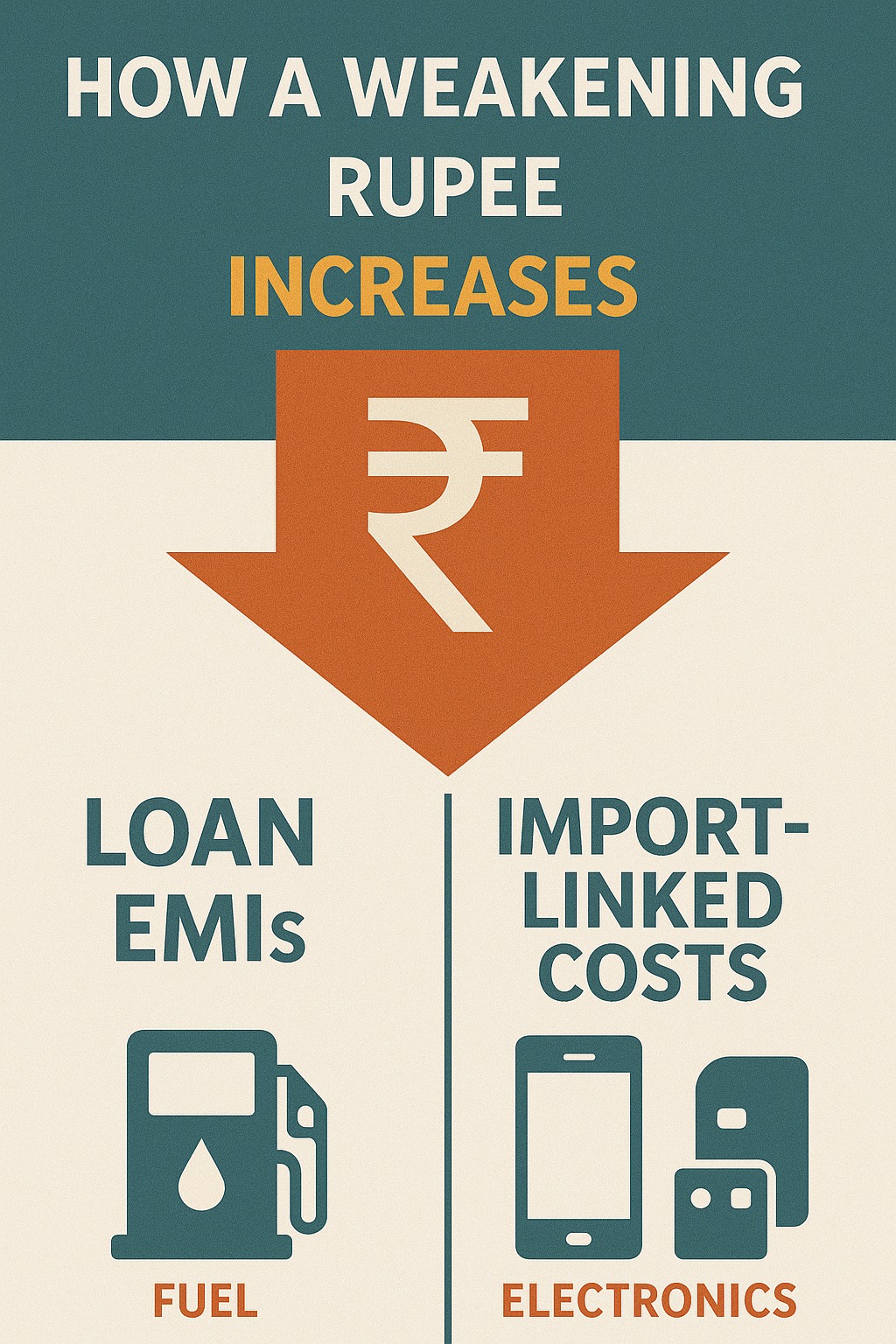
A weakening rupee increases inflation and imported commodity costs, which can push banks to raise lending rates. This may increase EMIs for floating-rate home, auto and personal loans. Import-linked expenses—like fuel, electronics, foreign study and travel—also become costlier when the rupee falls.
Introduction
The Indian rupee has slipped again against the US dollar—triggering concerns for consumers, borrowers, and businesses.
While currency fluctuations affect everyone differently, one thing is clear:
👉 A weaker rupee can increase your loan EMIs and raise prices of import-linked products.
This blog breaks down the real impact on your EMI, inflation, gadgets, fuel, travel, and everyday costs, in a simple, human way.
Why the Rupee Is Weakening — The 2025–26 Reality
The rupee typically weakens due to:
Higher crude oil prices
Strong US dollar globally
Foreign investor outflows
Geopolitical uncertainty
India’s import-heavy trade structure
Higher US Fed interest rates
When the rupee falls, India’s import bill rises → inflation rises → RBI becomes cautious.
This directly affects your EMI, daily costs, and financial planning.
How Rupee Depreciation Affects Your EMI
A weakening rupee increases inflation and forces RBI to:
Delay rate cuts
Or even increase policy rates in extreme cases
Banks respond by increasing:
RLLR (Repo Linked Lending Rate)
MCLR (Marginal Cost of Funds Lending Rate)
Base rates for floating loans
📌 Result:
Your floating-rate EMI can increase.
Real EMI Impact Example (If Rates Rise by 0.25%)
₹20 Lakh Home Loan (20 years)
Old EMI: ₹17,212
New EMI (0.25% higher rate): ₹17,551
📉 Increase: ₹339 per month
₹50 Lakh Home Loan (20 years)
Old EMI: ₹43,030
New EMI: ₹43,878
📉 Increase: ₹848 per month
₹10 Lakh Personal Loan (5 years)
EMI increases by: ₹150–₹220
Even small hikes in interest rates increase long-term EMI burden significantly.
Import-Linked Costs That Rise When Rupee Weakens
India imports several essential products.
A weaker rupee increases their cost for everyone.
1. Fuel (Petrol, Diesel, LPG)
India imports 85% of its crude oil.
When rupee falls:
✔ Fuel gets costlier
✔ Transportation charges rise
✔ Food inflation increases
✔ Logistics prices shoot up
2. Smartphones, Laptops & Electronics
Most components are imported.
Rupee depreciation increases:
Phone prices
Laptop costs
LED TVs
Imported gadgets
Repair part costs
3. Foreign Travel Costs
Rupee fall impacts:
Flight tickets
Hotel rates
International tuition fees
Forex card reload costs
Overseas shopping/expenses
Expected increase: 3%–7% depending on currency swing.
4. Imported Food & Essentials
Items like:
Chocolates
Coffee
Dry fruits
Packaged snacks
Premium FMCG
become more expensive.
5. Car Prices (Imported Components)
Even Indian cars use imported parts.
Rupee weakness increases:
Spare parts
High-end car prices
EV battery costs
Rupee Weakening — Who Gets Hit the Most?
Biggest impact on:
✔ Floating-rate home loan borrowers
Rates move every 3/6/12 months.
✔ Foreign-travelers & students
Everything from tuition to rent rises.
✔ Gadget buyers
Electronics become expensive.
✔ SMEs importing raw materials
Margins shrink.
Expert Commentary
“The biggest risk of a weakening rupee isn’t the currency itself—but the inflation it fuels. Not only do everyday costs rise, but lenders respond by raising interest rates, increasing EMI pressure on households.”
— N. Shah, Senior Forex & Banking Analyst
How Borrowers Can Protect Themselves
✔ 1. Keep FOIR below 40%
Avoid EMI overload.
✔ 2. Shift to part-prepayment strategy
Reduces impact of future rate hikes.
✔ 3. Maintain strong credit score
Gets you lower rates.
✔ 4. Avoid unnecessary imports
Delay gadget purchases if possible.
✔ 5. Consider fixed-rate loans (if risk-averse)
Stability during volatile periods.
Summary Box
Rupee fall → higher inflation
Inflation → RBI delays rate cuts
RBI stance → banks increase loan rates
Floating-rate EMIs may rise
Import-linked products get costlier
Borrowers must plan finances carefully
Vizzve Financial helps borrowers get the lowest interest loans even during volatile economic periods — with quick approvals, balance-transfer options, and smart EMI guidance.
👉 Apply now at: www.vizzve.com
❓ FAQs
1. Will my EMI increase if the rupee weakens?
Yes, if floating-rate loans get revised upward.
2. Does RBI increase rates when rupee falls?
Not always, but may act if inflation rises.
3. Which loans get affected first?
Home loans (floating), business loans, some flexible personal loans.
4. Does import cost always rise when rupee falls?
Yes, as importers pay more dollars per rupee.
5. Should I switch to a fixed-rate loan?
Only if you prefer EMI stability.
Conclusion
A weakening rupee affects your finances more deeply than you think—from EMIs to gadgets, fuel, travel, and household expenses.
Borrowers must stay alert, track RBI policy, and optimise their loans before rates rise further.
Published on : 7th December
Published by : SMITA
www.vizzve.com || www.vizzveservices.com
Follow us on social media: Facebook || Linkedin || Instagram
🛡 Powered by Vizzve Financial
RBI-Registered Loan Partner | 10 Lakh+ Customers | ₹600 Cr+ Disbursed